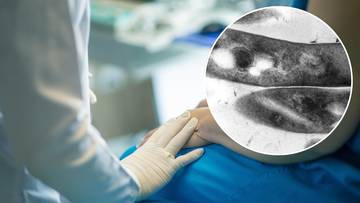
The World Health Organization has released a new report showing that approximately 8.2 million people around the world contracted tuberculosis last year alone. This is the highest rate since 1995, when the organization began global surveillance of the disease.
Compared to 2022, when 7.5 million cases were diagnosed, this is an increase of more than 700,000 cases. The organization also estimates the total number of sick people, including those not registered in the health system, to be around 10.8 million.
See also: Tuberculosis vaccine prevents coronavirus infection
This means that tuberculosis has overtaken COVID-19 as the leading cause of death from infectious diseases.
Increase in tuberculosis patients. More than 1 million deaths per year
In 2023, 1.25 million patients died from tuberculosis. According to the WHO, this number is lower than in 2022, when 1.32 million people died from tuberculosis, but eradicating the disease is still a long way off.
Reference: WHO: 30 tuberculosis cases per hour in European region
The increase in the number of cases is such that 98% of these cases are diagnosed in low- and middle-income countries where health services are underfunded.
Most infections were detected in India (26%), Indonesia (10%), China (6.8%), the Philippines (6.8%) and Pakistan (6.3%). These five countries together account for 56%. diseases around the world. More than half of those who develop tuberculosis are men (55%), 33% women and 12% – children and young people.
According to WHO experts, a significant number of new TB cases are caused by five main risk factors: malnutrition, HIV infection, smoking (especially in men), diabetes and alcoholism.
Tuberculosis – symptoms and treatment
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infection caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which most often attacks the lungs but can also spread to other organs, such as the kidneys, spine, and brain.
The disease is spread through droplets, that is, through contact with microorganisms released when a sick person coughs, sneezes, or speaks.
See also: USA: Woman suffering from tuberculosis refuses treatment. she went to jail
Symptoms of pulmonary tuberculosis include chronic cough, often coughing up blood, weight loss, fever, and profuse sweating at night. This disease can occur for a long time without any obvious symptoms, making early detection difficult. Without proper treatment, tuberculosis can lead to serious health complications and even death.
Tuberculosis can be treated. Standard treatment involves taking several different drugs at the same time to prevent bacteria from developing drug resistance. The most commonly used preparations are isoniazid, rifampicin, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol.
Your browser does not support video players… Read more
Source link

